
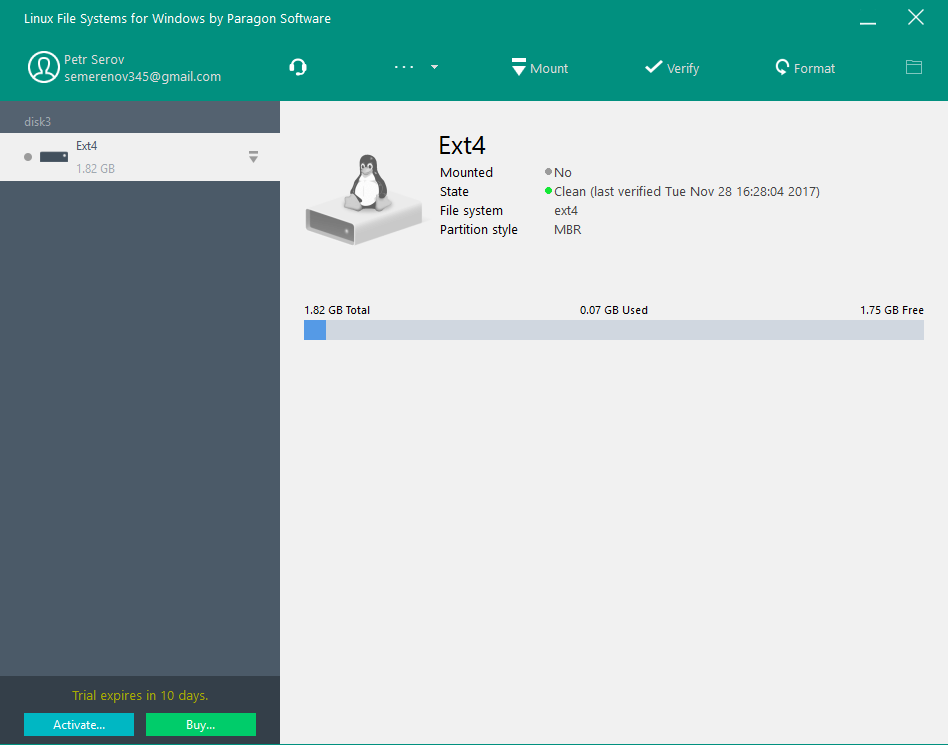
However, feel free to use a different filesystem formats if it suits your needs.įollow the above steps for all your target partitions. If you plan to use the partition with other operating systems, then it is better to use fat16/fat32. For Linux, ext3/ext4 is the most appropriate filesystem format. Right click on the target partition, then click “Format to” and select the target filesystem format. The target partition to format is /dev/sda5. In our case, there’s only one disk connected. First, select the appropriate disk from the top-right corner. The image below shows the main window of GParted. GParted requires root permission to launch because it makes system-level changes. (Click here to learn how to make a bootable USB flash drive from an ISO.) To do so, you must make a bootable USB flash drive. GParted can also be used through live CD/USB regardless of your distro, and you can find the official GParted live ISO here. GParted does not come pre-installed with most Linux distros, but you can install it by using the appropriate installation command for your Linux distro. GParted allows you to resize, copy, and move partitions without data loss, and it allows you to rescue data from lost partitions. To show you how to carry out this process, we will use GParted: an open-source partition editor that offers an organized UI for managing disk partitions.

This method is probably more usable for most Linux users because it provides a user interface and explains the process at each step. However, before you begin, make sure that there are no data in the partition that you are afraid to lose. Formatting disk partitions on Linuxĭepending on the tools being used, the formatting process can be carried out in two ways. In this article, we will show you how to format disk partitions on Linux, assuming that you have already created the target partition. Within the operating system, a partition may make it seem as if multiple drives are connected, as each partition comes with its own filesystem and storage capacity.Ī partition must be formatted to prepare it for use, but a partition can also be formatted to erase all its data, to establish a different filesystem, or to fix errors. However, modern operating systems allow physical storage systems to be divided into multiple logical storage systems. In most cases, a storage device comes with a single partition. A partition is the storage space on a hard drive that has been designated for a certain purpose.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
